A few applications of the Zener Diode are the protection of DC, electronic protection of AC, reference voltage in electronic circuits, voltage limiters in Op-amp circuits, voltage shift, clipping circuits, etc.
I will explain the function of these applications of Zener diodes in electronic circuits in this article, and also some special uses of Zener diodes as per my projects and products.
The table of contents in this article is as follows
Applications of the Zener diode in over-voltage protection
Refer to Figure 2. A thyristor is connected across the power supply (AC or DC). A Zener diode is connected between the anode and the gate of the thyristor. The resistor between the gate and cathode is for noise suppression only for the thyristor.
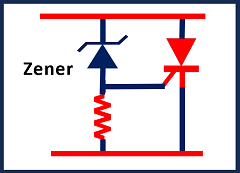
When the instantaneous voltage across the thyristor (or supply voltage) becomes more than the Zener diode voltage, then a current in the gate of the thyristor flows. And thyristor becomes ON. It is like a short circuit. Then, a fuse can be used to protect the circuit.
For the AC circuit, we need two such circuits in anti-parallel for voltage protection in both directions.
Also, I will explain another application of this circuit in the last part of the article, as on my experience with this article.
Applications of the Zener diode as a voltage reference in a comparator circuit
Figure 3 shows a simple comparator circuit. One of the applications of the Zener diode is to provide a voltage reference in a comparator circuit. Zener provides the reference voltage at the non-inverting terminal of the op-amp.
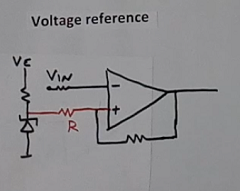
The resistor R (red color) in between Zener and the non-inverting terminal of the op-amp provides the necessary hysteresis to the comparator circuit. The hysteresis concept does not work without this resistor.
The advantage of using Zener in place of a resistor divider here is explained in detail last part of this article as per experience.
Use of a Zener diode for protection in the op-amp circuit
Figure 4 shows a simple op-amp circuit as an amplifier. Where the gain of the circuit is R2/R1.
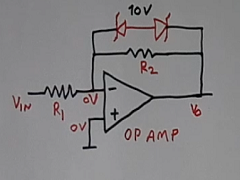
the op-amp circuit
If the voltage at the input is higher, then the op-amp may go into saturation. And the voltage of the inverting input also increases. This creates some problems in certain applications, like control. To avoid this problem, two Zener diodes in series with reverse polarity directions (we call them back to back) are connected as per the figure.
This arrangement will limit the output voltage of the op-amp circuit. This voltage limiting value will be a little more than 10 volts with a 10-volt Zener diode. It will be about 10.5 volts due to the forward voltage drop of another Zener diode in series.
This arrangement also protects the op-amp, and it is one of the very useful applications of the Zener diode in electronic circuits.
Applications of the Zener diode as a voltage regulator
A simple circuit for the application of the Zener diode as a voltage regulator is shown in Figure 5. If the input voltage is changing, then we also get a fixed voltage Vo, at the output across the load resistor, R. This fixed output voltage will be equal to the Zener diode voltage.
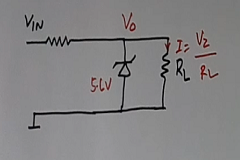
If the voltage of the Zener diode is 5.6 volts, the output voltage will be 5.6 volts. The total current flowing in the load will also flow in the resistor at the input. So there will be heavy energy loss and also a voltage drop at the input resistor.
In the case of the open circuit at the output (no load resistor), the heavy current flow of the load resistor will go to the Zener diode. So the current range of this type of voltage regulator is very, very low.
An improved version of using the Zener diode in the voltage regulator is shown in Figure 6.
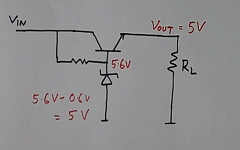
In this circuit, only a small current flows in the Zener diode, and a transistor amplifies the current. So this circuit can give more current to the load. The output voltage at the output will be less than the Zener diode due to the voltage drop in the base-emitter of the transistor.
If the Zener voltage is 5.6 volts, and the BE drop in the transistor is 0.5 volts. Then the output DC voltage of the regulator is equal to 5.6 – 0.5 = 5 volts in this type of circuit application of a Zener diode.
Use of Zener diode in Voltage shifting
The voltage shift circuit is as per Figure 7. The input voltage at Vi is increasing with time (black color waveform, right side). Then the output voltage Vo across the resistor R will be less than the input voltage (see red colour waveform) all the time.
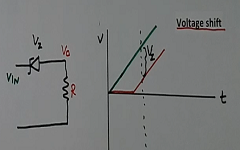
This difference in the voltage between the input and output will be equal to the Zener diode voltage.
Clipper circuit with Zener diode
One of the applications of the Zener diode is as per Figure 8. Two Zener diodes are connected in series. They are in a series with back-to-back arrangements. A resistor is also connected in series.
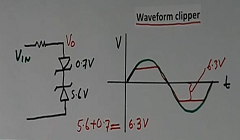
If the voltage of the Zener diode is 5.6 volts, then the total voltage of both the Zener diodes in series will be about 5.6 + 0.7 = 6.3 volts.
So clipping voltage will be 6.3 volts in this circuit in both directions of the AC. If we give AC at the input (Black colour waveform), then the output voltage will clip to 6.3 volts (red color waveform).
Extra knowledge as per experience
In this part, I explain some interesting points about the applications and uses of the Zener diode as per my experience.
Noise Problem
In Figure 3, a Zener diode provides the reference voltage. Many times, we use only a resistor divider for the reference voltage. Even I was using only a resistor in the beginning (with no experience).
However, with a resistor divider only, the circuit becomes very sensitive to noise. If there are any noise spikes (this is almost always the case in complex circuits) at the DC power supply of the op-amp, then the reference voltage will also have noise. Then the output of the comparator will switch unnecessarily sometimes.
The Zener diode solves this noise amplification problem.
Protection using a Zener diode and a thyristor without a fuse
In the protection circuit as per Figure 2, I suggested a fuse. However, in one of our projects, we did not use the fuse. So it was providing a total short circuit across the open winding of the current transformer. So it behaves as a protection for the open circuit in the current transformer.
This thyristor Zener diode circuit can also be used for making a DC power supply without a transformer (but without isolation).
The failure of the Zener diode is very common. So, a slightly higher watt type Zener diode should be used in all the above circuits except for the op-amp circuit. The watts of the Zener diode will increase with a series connection. We get very little advantage from more watts of parallel connections of the Zener diode. But we get better reliability in parallel connections of the Zener diode.
High noise problem
Further, one of the applications of the Zener diode is in filtering high noise in the power supply. Now refer to Figure 9. We used this circuit in one of our projects for power supply protection. The noise level was very high in that project. The RC time constant acts as a low-pass filter in this circuit. And Zener provides overvoltage protection.
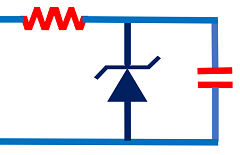
However, due to a resistor being a series, there will be a voltage drop in the resistor. So the output voltage will become a little unregulated in this arrangement.
But for us, noise filtration was more important than regulation. And we specially designed the electronic circuit suitable for a little unregulated voltage supply.
For more knowledge, watch the following video on the applications of the Zener diode.

Also, read the article on Zener diodes in series and parallel
Keep learning by reading about the application of autotransformers.
Also, read Applications of the Diode.
Further, read How Optocoupler works.
Also, read how the current transformer works.
I hope that you enjoy this article on “Applications of the Zener diode”.
If so, then subscribe to my YouTube channel.
About the author – G K Agrawal B.Sc and B.Tech (from HBTU Kanpur), Retd. Sr DGM Design (BHEL), the inventor of patents, has lifelong industry experience in the electrical and electronics design field of R&D. He worked for BHEL. He shares his experience and knowledge on blogs and YouTube. Read the profile here.


Excellent information in this technical article.
avery nice explanation.
Nice post. I learn something new and challenging on websites I stumbleupon every day. It will always be useful to read through articles from other writers and use a little something from other websites.
Learning is a great idea. I am 68, but still learning and also spreading knowledge through this website and Youtube also.